
In 2020, Apple began another transition, this time from x86 to the ARM-based Apple silicon. Since then, the system went through several architecture transitions, first from PowerPC to Intel x86 in 2006.
#OSX VERSIONS MAC OS X#
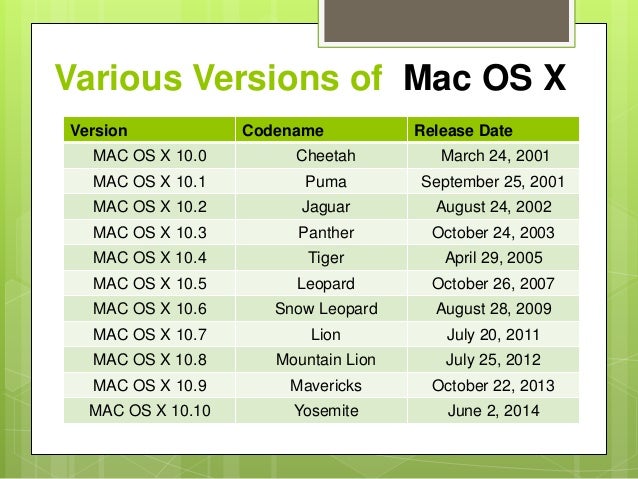
The classic Mac OS was eventually succeeded by Mac OS X in 2001 with the release of Mac OS X Cheetah. The Unix core of NeXTSTEP was renamed to Darwin, released as open source and in the following years, it was modernized partially by using code from FreeBSD and other projects. As a part of the deal, Apple gained NeXT's object-oriented operating system called NeXTSTEP based on Unix. Apple eventually saw the solution in buying out NeXT in 1997, the company founded by Steve Jobs after he was ousted from Apple.

During Apple's transition from Motorola 68k series to the PowerPC architecture, Mac OS was also ported to the new platform by using emulation, until a new, native OS was developed as a part of the Copland project.Īfter the failure of Copland, however, Apple was forced to further maintain the original Mac OS codebase, which no longer satisfied the ever-increasing performance and stability requirements. In its early versions, it only supported running a single application at a time, although it was later extended with cooperative multitasking support via MultiFinder. The system from the very beginning made use of a graphical interface, similar to the one used by the earlier Lisa. It was first introduced together with the original Macintosh in 1984. MacOS is a series of operating systems developed by Apple for their Macintosh platform. Proprietary (with open-source components) Closed source (with open source components)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
